Unlocking the Full Potential of Batteries and Hydrogen Technologies
Principle of EIS
Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy involves applying an alternating current (AC) voltage signal to an electrochemical system, such as a battery or an electrolyzer/fuel cell, and measuring the resulting current response over a range of frequencies. This analysis of the frequency-dependent response reveals the chemical and physical processes within the system, providing complex impedance plots that help extract information about the system’s properties and behavior.
EIS Benefits
EIS is a non-destructive technique bridging the gap between steady-state and transient-state electrochemical studies. It enables researchers to investigate electrode kinetics during discharge or recharge stages. This information improves the understanding and control of chemical processes in energy storage devices, enhancing performance, efficiency, and durability. EIS can identify issues related to material layers, charge transfer, diffusion effects, and electrolyte conductivity, optimizing the design, materials, and manufacturing processes of batteries and hydrogen technologies, leading to improved performance and lower costs.
Batteries and Hydrogen Technologies
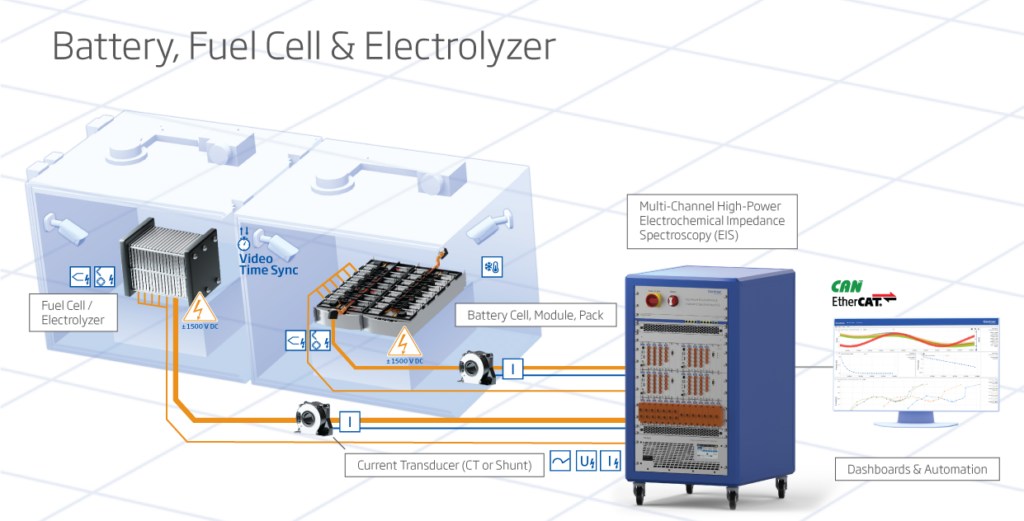
EIS applies to a wide range of electrochemical systems, including batteries and hydrogen technologies like fuel cells and electrolyzers. In batteries, EIS studies electrode reaction kinetics, monitors internal resistance and capacitance changes, and detects capacity fade and degradation mechanisms. This helps optimize battery performance, lifespan, and safety, leading to more efficient and durable energy storage solutions. In hydrogen technologies, EIS provides insights into hydrogen production and storage processes. It studies water-splitting reactions in electrolyzers, monitors fuel cell electrode performance, and detects changes in hydrogen storage materials. This aids in developing efficient, cost-effective, and sustainable hydrogen technologies.
Challenges and GI Benefits
EIS requires specialized instrumentation and can be time-consuming and computationally intensive. Achieving a balance between measurement speed, accuracy, and cost is a key challenge in the design and implementation of EIS systems. Gantner Instruments addresses these challenges with its innovative all-in-one EIS data acquisition and analysis solution, providing efficient, cost-effective, and accurate insights to unlock the full potential of batteries and hydrogen technologies.
Integration with Q.series X
Integrate EIS seamlessly with the Q.series X data acquisition system, providing a comprehensive solution for monitoring and analyzing electrochemical systems. The Q.series X offers high-speed data acquisition, modular expandability, and integration with existing infrastructure, making it an ideal platform for EIS studies.
Gantner Instruments’ all-in-one EIS solution exceeds all standard requirements of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy through its robust design and advanced technical features. The system includes a high-performance Q.series X A193 module, designed for high-power and industrial applications, with capabilities for signal amplification and offset measurement that enhance sensitivity and selectivity in impedance measurements. The voltage measurement range and current measurement flexibility, supported by robust galvanic isolation, ensure accurate and reliable data collection across various applications, including entire battery packs. Synchronous signal collection maintains data coherence and accuracy, utilizing the Lock-In technique to isolate specific signal frequencies and phases, essential for detecting weak signals in noisy environments. The system’s broad frequency range from 1 mHz to 10 kHz and modular configuration, scalable up to 128 EIS channels, make it suitable for diverse electrochemical testing requirements. Comprehensive data accessibility and real-time visualization tools, including Nyquist and Bode plots, facilitate detailed analysis and immediate feedback. Advanced connectivity options, such as an open API and EtherCAT interface, ensure seamless integration with existing power systems and automation setups. Additional features like high-isolation thermocouple inputs, temperature measurement channels, and an air deflector for heat management further enhance system performance and reliability, making Gantner’s EIS solution a comprehensive and efficient tool for optimizing batteries, fuel cells, and electrolyzers.
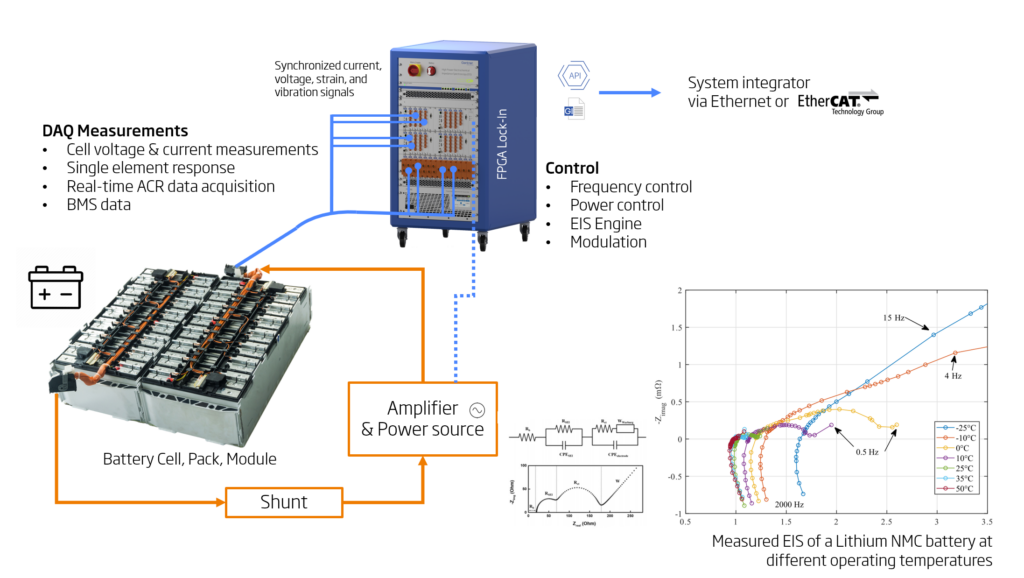
Unlock the Potential of Next-Gen Battery Storage with Advanced EIS
Explore how Gantner Instruments’ cutting-edge Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) solutions help maximize performance, enhance longevity, and deliver unparalleled insights for next-generation battery storage technologies.
More articles
Gantner delivers DAQ for Open Rotor Engine
Gantner Instruments has delivered its Q.series data acquisition system for a major research programme exploring Geared Pusher Open Rotor engine designs, with the goal of achieving a 20% reduction in fuel consumption and CO2 emissions.
Read more...Huge Wind Turbine Blade Tests at BLAEST
The world’s longest rotor blade was manufactured by LM Wind Power in Denmark. Planning the test of the 290 ft (88.4 m) long rotor blade began in 2015. With BLAEST (the Blade Test Centre) Tests are now underway together in Aalborg, Denmark.
Read more...Monitoring Solutions for Asset Management
Gantner Instruments provides monitoring solutions for both static and dynamic equipment in terms of vibration monitoring of piping, vessels, heat exchanger, large machines (static) and pumps, fans, and turbines (dynamic). Based on the robust and flexible Q.series modules with its decentralized signal conditioning and data acquisition modules, a very reliable and cost effective trend and condition monitoring solution is available and working also under harsh environmental conditions. With the monitoring solution of Gantner Instruments the asset becomes smart and delivers detailed status information.
Read more...Innovation Call with CEO Werner Ganahl of Gantner Instruments
State funding for seven future digital projects The best digital innovation projects in Vorarlberg have been sought and funded. Seven projects are receiving a total of 130,000 euros in state funding.
Read more...