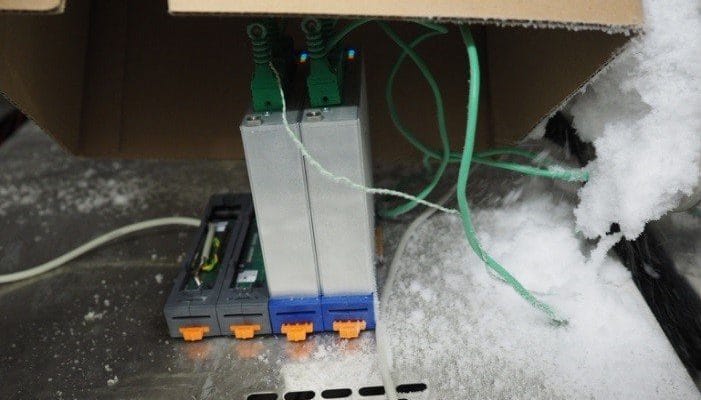
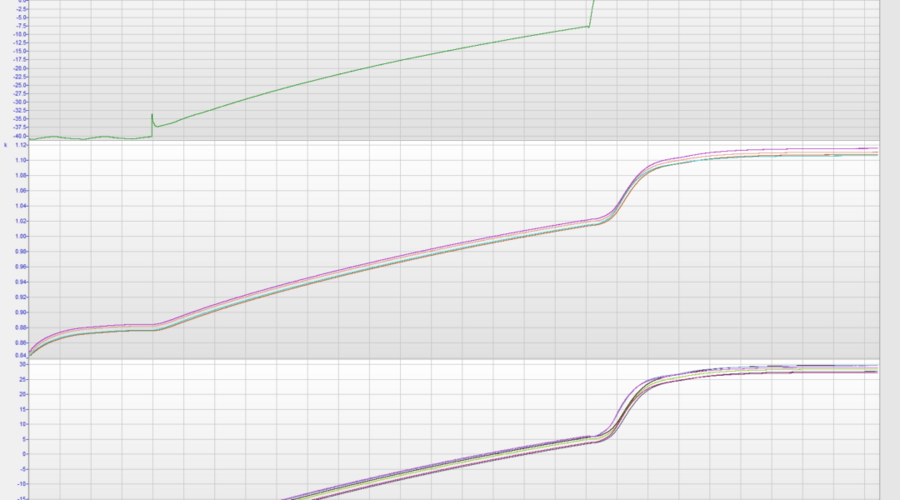
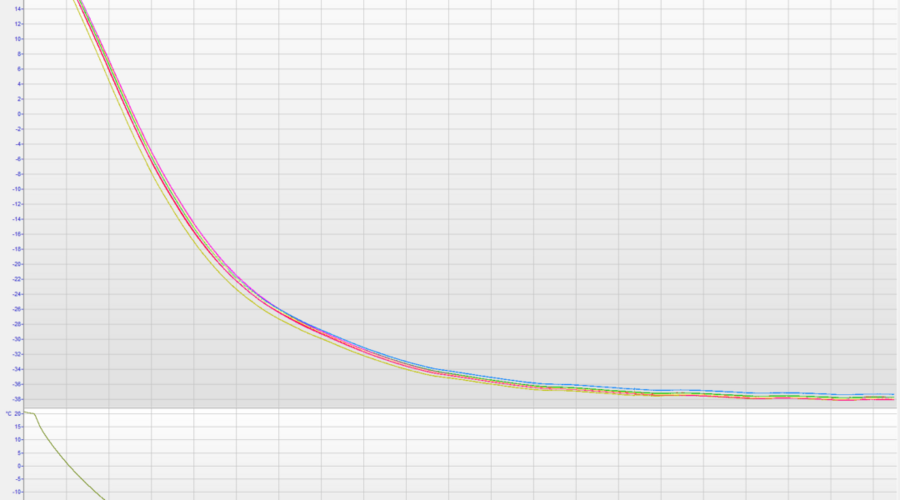
The Q.bloxx XL A104 TCK provides 8 channels for thermocouples (here as Type K, NiCr/Ni) with standard miniature front sockets.
During a day in the climate chamber at -40°C it was completely frozen. After connecting with power supply to the I/O module it was delivering stable and precise measurement values. When temperature was increasing it passed dew point. We observed no impact on the measurement quality or from condensation during this phase. Our I/O module passed this test successfully – even when the datasheet recommends only -20°C operating conditions.
More articles
Q.series X D101 SV: Digital Measurement Module with Sensor Supply
The Q.series X D101 4 x Lemo 2B SV from Gantner Instruments is a digital measurement module that has been engineered to facilitate a broad spectrum of digital signal processing tasks. It is designed with a focus on providing accurate and rapid data acquisition for industrial applications that require high-performance measurement capabilities with integrated sensor excitation.
Read more...Project State Overview – Real-time Visibility and Control with GI.bench
Engineers managing complex test setups know the frustration of hunting through countless data files, sensor channels, and historical records. The new Measurement Explorer in GI.bench addresses this challenge head-on, streamlining data management into a unified, intuitive, and fast user interface.
Read more...How strong are you? 💪🏼
Such was the question asked by electronics apprentice Fabio Rudigier when determining a suitable topic for his final project as part of his final apprenticeship examination. He wanted to develop a machine that measures the force applied by an arm press and displays it visually on a display device.
Read more...Introducing the Q.series X A12x 1500V Plus Versions
Gantner Instruments expanded the A12x module lineup with Plus versions (e.g., Q.series X A128 Plus SEB) that feature an increase in their voltage capacity up to 1500V, meeting the evolving demands of industries that require higher voltage limits for testing and measurement. Let's delve deeper into the enhanced capabilities of the A12x module lineup and how they empower engineers across various industries.
Read more...
