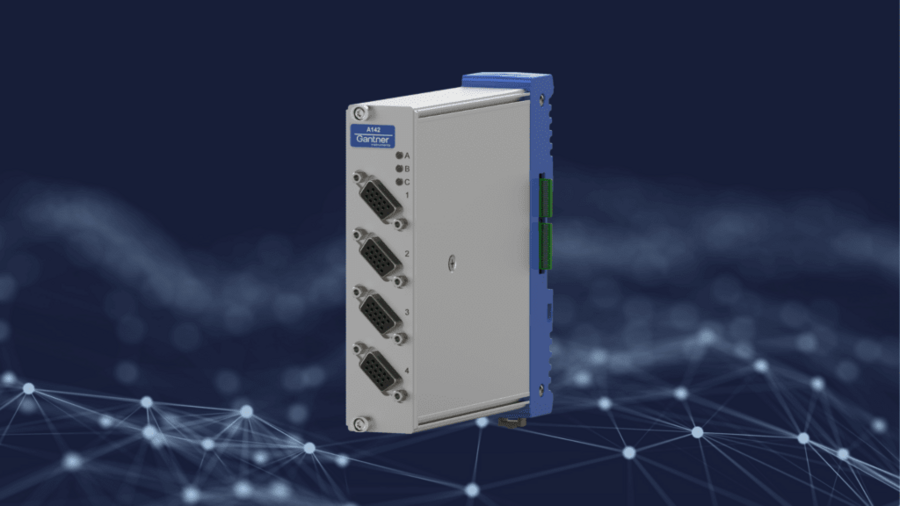
You can acquire data and control your testing operations with Q.series X systems. With the introduction of our new Q.series X A142, we have extended our capabilities for force and motion control applications. The Q.series X A142 is a universal input and output module designed with closed-loop control applications in the field of automotive, aerospace, and mechanical testing in mind. It features all sensor interfaces typically found on a hydraulic, pneumatic, or electric test actuator. By combining with an onboard 10 VDC analog output and test.con’s PID controller functionality, you can turn your Q.series X system into an integrated data acquisition and control solution for any force or motion control application.
The A142 comes with three 18-Bit, 20 kHz analog inputs (SAR ADC). You can use two inputs for LVDT/RVDT sensors or strain gage-based transducers, allowing you to use dual-bridge load cells for critical force control applications. The third analog input is a 10 VDC voltage input that can be freely configured for, for example, a potentiometric sensor or an external function generator as input for the PID controller. An additional Synchronous Serial Interface (SSI) makes the A142 unique. SSI is a point-to-point serial communication standard for digital data transmission between a master and a slave. SSI is commonly used with absolute encoders, as well as with Temposonics position sensors from MTS Sensors.
What is SAR ADC?
The method of Successive Approximation Register (SAR) is a method used in A/D converters for converting the analog signal into a digital signal. It is based on the comparison of the analog input voltage with a reference voltage. In successive approximation, the comparison is made step by step and is repeated continuously, whereby the reference voltage is changed so that it increasingly approaches the input voltage. Unlike a sigma-delta ADC, the SAR architecture does not have latency. The relatively high sample rate and zero-latency make the SAR ADC suitable for closed-loop control applications.
Key Features:
- 2 Analog inputs for strain gage transducers or LVDT/RVDT sensors
- 1 Synchronous Serial Interface (SSI)
- 1 10 VDC analog input
- 1 10 VDC analog output
- 4 Digital inputs and outputs
- 20 kHz update rate
- Low-latency 18-Bit SAR ADC
- 500 VDC galvanic isolation for all analog inputs
- Onboard virtual channels for scaling, filtering, and calculations
- Available in Q.bloxx X, Q.brixx X or Q.raxx X packaging
- Optionally as EtherCAT slave module (XE version)
- 15 Pin standard D-sub connectors
Read more about our Q.series X Data Acquisition System here.
More articles
GI.training in NRW in May 2026
We will be in North Rhine-Westphalia for the GI.basic training on May 12, 2026, and for the GI.professional training on May 13, 2026.
Read more...Monitoring Solutions for Asset Management
Gantner Instruments provides monitoring solutions for both static and dynamic equipment in terms of vibration monitoring of piping, vessels, heat exchanger, large machines (static) and pumps, fans, and turbines (dynamic). Based on the robust and flexible Q.series modules with its decentralized signal conditioning and data acquisition modules, a very reliable and cost effective trend and condition monitoring solution is available and working also under harsh environmental conditions. With the monitoring solution of Gantner Instruments the asset becomes smart and delivers detailed status information.
Read more...A Step Closer to Near-Supersonic Train Travel
South Korea’s hyperloop train reaches over 1,000 km/h in recent tests.
Read more...The Story Behind GI.blop: A home-brewed NEIPA Christmas treat from Austria
Christmas is approaching, and with it comes the festive season of sharing and special gestures. This year, we at Gantner Instruments wanted to give our customers and partners something unique for the holidays. So we created a special handcrafted beer we call GI.blop that is not only a great gift but also tells a story.
Read more...
