Due to its large size, the maintenance services are divided into strategic areas to serve the 16 existing lines optimally and exclusively. A breakdown in a train can jeopardize the proper functioning and punctuality of a line. That is why the maintenance service needs to have technological test tools to anticipate problems through predictive maintenance.
Based on periodic, systematically conducted braking performance tests, Metro de Madrid can reliably and safely roll out condition-based maintenance.
A series of measurements on three different braking systems (pneumatic brake, electrical brake, and emergency brake) lets Metro de Madrid better plan their maintenance cycles and deploy their predictive maintenance concept.
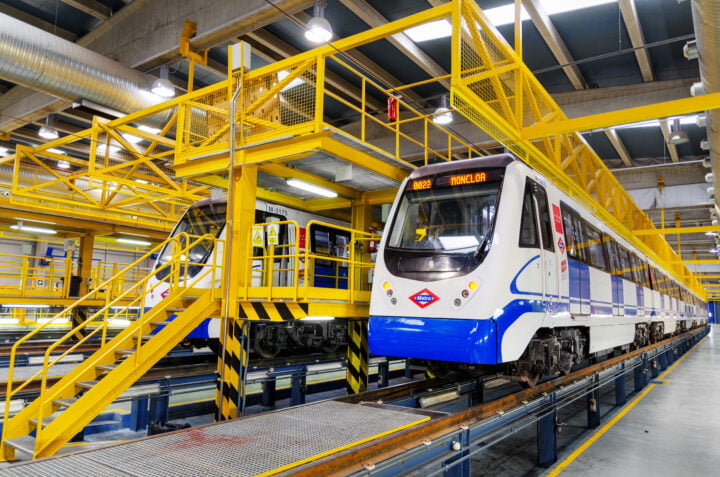

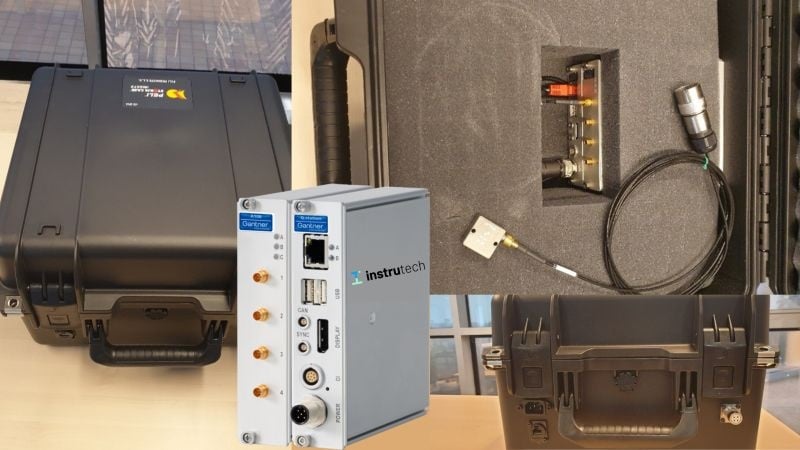
To perform brake testing on a total of 276 different metro cars, Metro de Madrid required a precise, robust, and portable system that it could install on the different trainsets. The portable and rugged Q.brixx X system proofed to be the ideal system for this application. A Q.brixx XL A108-4M1 measurement module acquires an acceleration signal from a Dytran series 7577 high precision MEMS sensor. The signal is sampled at a rate of 100 Hz, and unwanted noise is then filtered out with a fourth-order lowpass Butterworth filter. For improved robustness, the Q.brixx X system is installed inside a custom-made Pelicase.

Before the braking test, the metro car is placed on a horizontal track, and the accelerometer offset is eliminated. The metro then performs an acceleration and deceleration cycle. The braking and rest endpoints are selected for each cycle. The average steady-state acceleration and deceleration values are then calculated. Next, the average acceleration value during the rest phase after the braking is calculated. This value represents the mean value. Finally, the average deceleration is calculated as the absolute value of the difference between braking deceleration and rest acceleration.
For user convenience and to ensure test repeatability, instrutechSOLUTIONS developed a custom software application. The application was written in Python, benefiting from the open and flexible interfaces known as GI.connectivity, which came free of charge with the DAQ system. The Python application allows setting the accelerator offset, displaying the measured acceleration/deceleration signal, and providing a pass/fail indication for the average deceleration measured during brake testing.

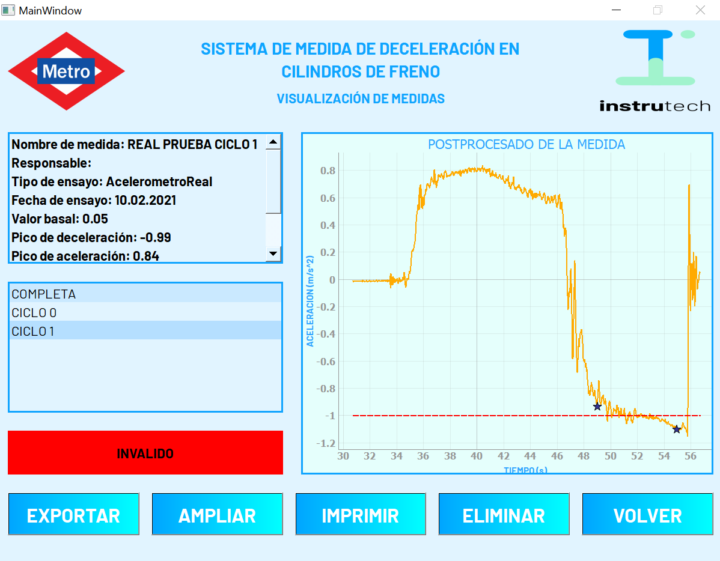
This test & measurement application showcases the versatility of Gantner’s Q.series X data acquisition system. Combining of a flexible and modular hardware platform, in combination with reliable data exchange and interoperability through various read/write interfaces, makes Gantner Instruments one of the most sought-after companies for data acquisition systems.
Modules used:
- 1x Q.brixx X station B
- 1x Q.brixx XL A108-4M1
- 1x GI.bench Data Acquisition Software

More articles
Our new fiber optic measurement – without the hassle
Fiber optic measurement methods come with the advantage of being insensitive to interference from the environment. We all know that. What we also know is that actually using them in test and monitoring projects was not so easy so far. Either because there were steep learning curves or simply no integrated DAQ solution available. However, we have great news for you!
Read more...Innovative EIS Solution for Next-Generation Battery Storage Systems
Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) is an analytical tool for anyone involved in the development, maintenance, and advancement of electrochemical systems like batteries, fuel cells, and electrolyzers. Understanding EIS and its benefits can provide a substantial edge in optimizing these systems’ performance and longevity.
Read more...Q.series X D107 SV: Digital Measurement Module with Sensor Supply
The Q.series X D107 2 x Lemo 2B SV module from Gantner Instruments provides a comprehensive solution for digital signal acquisition and sensor supply needs. Designed for distributed installations requiring precise digital measurements, this module enhances the Q.series product family's robust offering.
Read more...Precise Temperature Measurement with Pt100
Temperature measurement is one of our key competence areas. Here we maintain a position of global leadership. Our advanced 4-channel Q.bloxx A105 measurement module sets new standards in terms of stability and precision. For many different applications, the extremely precise and stable measurement of temperatures is an absolute prerequisite for the control of processes or the success of product innovations. In addition to the essential precision, particularly important aspects of this are the maintenance of stability when changes occur in the ambient temperature and ensuring long-term stability.
Read more...