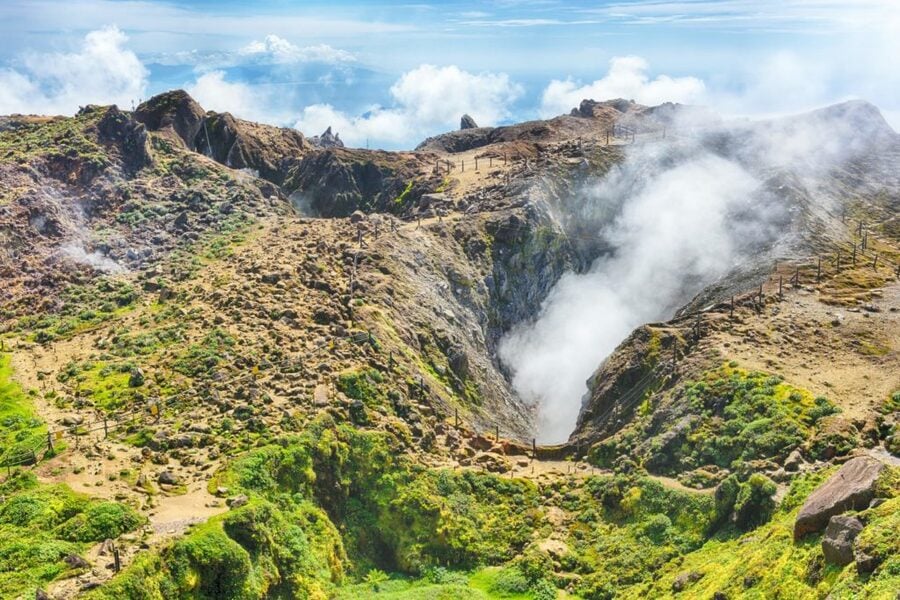
The team at Geosciences Rennes, a joint mixed research unit between the University of Rennes and the CNRS (UMR-6118), has been conducting monitoring experiments on the volcano La Grande Soufrière over the last 15 years. La Grande Soufrière is located in Guadeloupe, a French overseas region located in the southern Caribbean Sea.
In response to the volcano regaining activity since 2014, the Géosciences laboratory decided to increase their monitoring capacity on the top of the lava dome by deploying a network of sensors (e.g., Pt100 in fumaroles, 1D and 3D seismic geophones, thermocouples in the soil, pressure sensor and Pt100 in the boiling acid lake). The team’s previous positive experience with the Gantner Instruments’ e.series (e.reader, e.pac, and e.bloxx) led them to retain the Q.series to develop their new acquisition network.
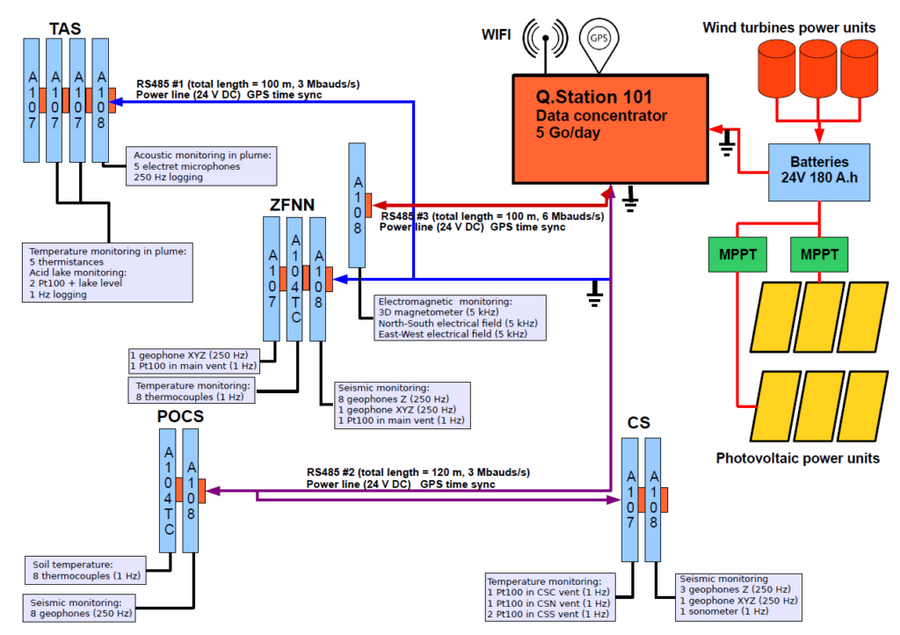
Figure 1 is a synoptic of the basic network at work since 2015: a Q.station 101 together with multiple Q.bloxx A108 and A107 modules distributed over three RS485 buses. Wind turbines and photovoltaic units provide electrical power to the network. A long-range Wi-Fi link is used to transmit the data to the volcano observatory located 10 km away. A GPS antenna is used to synchronize the Q.station, which is particularly crucial because precise time synchronization is needed to correlate the seismic data acquired with the geophones connected to A108 modules. Because of their versatility, A107 modules are used in the most active areas where multiphysics measurements are performed with either resistive, voltage, or current sensors. The A107 modules’ flexibility allows IPGP to test using their sensor prototypes in the measurement campaign.
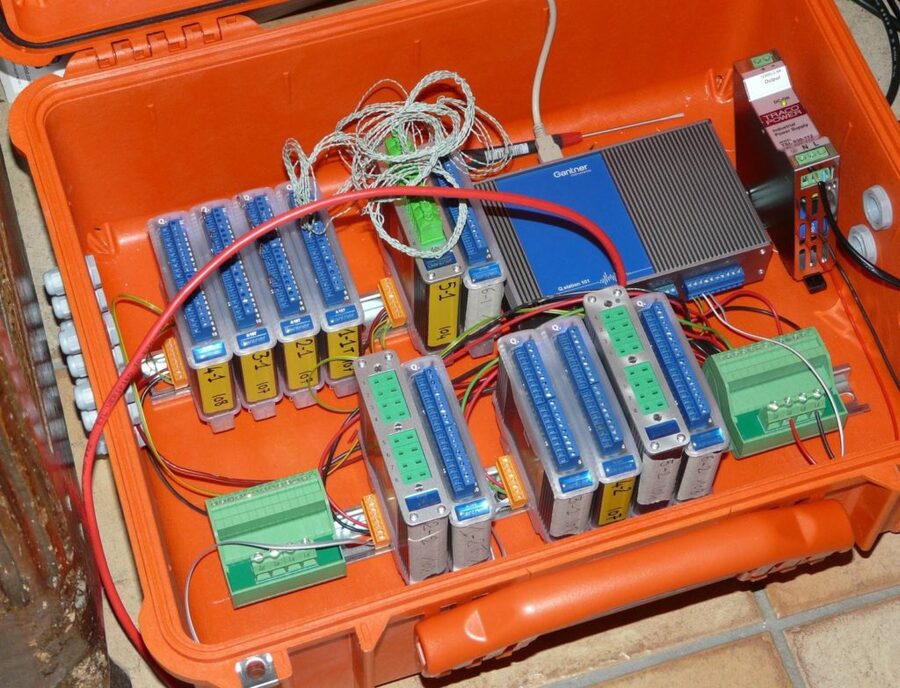
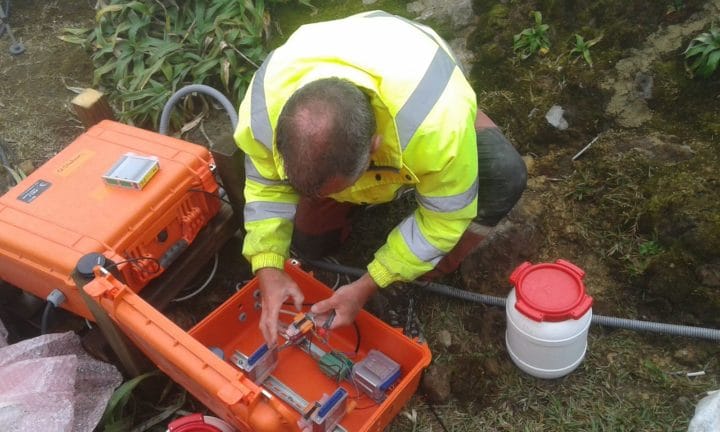


The environmental conditions at the top of the volcano are very harsh. The main difficulties are heavy tropical rain (8,000 mm per year), strong winds, lightning storms, and acidic gases emitted by fumaroles. Despite these harsh conditions, Gantner Instruments systems remain operational almost all the time. The systems are protected using a “double box” technique. The first box on the outside is used to protect against heavy rains and wind. The conditions inside this container roughly correspond to IP62 except for the acidic gases present. A Pelican case is then placed inside the first box, which contains the DAQ system and protects against humidity and acidic gases.
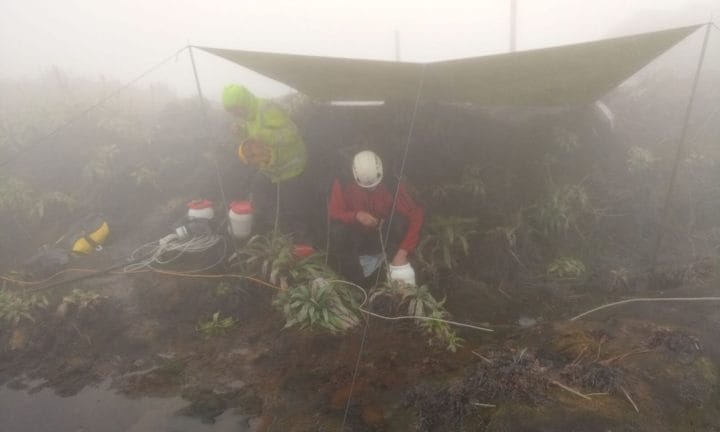

The Géosciences laboratory is currently improving its acquisition network by installing several Q.stations at different locations around the volcano. This solution reduces the lengths of the RS-485 lines that appear sensitive to lightning and the GPS time synchronization provides a common time base for all measurement data.
For an example of the scientific usage of the data acquired with the Gantner Instruments DAQ platform, you may consult our recent paper regarding “Abrupt changes of hydrothermal activity in a lava dome detected by combined seismic and muon monitoring” available online.
More articles
Fuel Cells: Advanced Measurement Techniques and Navigating the Hydrogen Market
The energy landscape is in a state of flux, shifting towards sustainable practices, and fuel cells have risen as a promising beacon of renewable energy. The mastery of fuel cells, their inner workings, and the nuances of their measurement, is central to this paradigm shift towards green energy. These devices, which are essentially electrochemical cells that transform chemical energy into electricity, promise a more sustainable, carbon-neutral future, provided we can harness their full potential. This blog post delves into the captivating scientific universe of fuel cell measurement, elaborating on the methodologies, complexities, challenges, and breakthroughs that make fuel cell technology so intriguing.
Read more...Enhanced Functionality with GI.bench’s Newest Release: Revamped UI, Powerful Tools and More!
Introducing the latest update to our powerful and intuitive testing and measurement software - GI.bench. This update promises to elevate your testing capabilities with features designed to streamline your workflow and maximize productivity.
Read more...EES Europe, Smart Energy Europe & Intersolar
EES Europe ist the largest international trade fair for batteries and energy storage systems in Europe. Over 450 energy storage companies will present energy storage systems in Munich.
Read more...GI.service Asset performance optimizer
With the significant investments being made in distributed renewable energies, the global energy market is changing from a central supply concept to a decentralized system. This transition is presenting companies in the energy market with various strategic and technical challenges to achieve efficient operations.
Read more...