The electric vehicle testing community is having to deal with increasingly complex products and faster development cycles, meaning that test labs are under constant pressure. As such, the ability to efficiently analyze test data has never been more critical. Costs must be kept as low as possible, while growing amounts of data from sensors are processed. Engineers must monitor and analyze test data in real time, regardless of how much there is to sift through. It’s therefore no wonder that they are seeking new ways to improve testing efficiency and reduce risk of low quality data.
During acquisition, electrical and mechanical signals are measured at sample rates in the kilohertz range and need to be highly synchronized. These tests in particular generate an overwhelming amount of data. The real challenge is storing and preserving this data. The handling of such large volumes of structured and unstructured data requires an adaptive and scalable data back end. To cope with ever-changing requirements, setup configurations, parameter extensions and sample rates, a separation between hot and cold datais helpful.
‘Cold data’, which is less frequently accessed and only needed for auditing or post-processing, is stored in a distributed streaming platform that scales as needed. The ‘hot data’, which is accessed in real time for analysis, is provided in a NoSQL time-series database. This database stores readings securely in redundant, fault-tolerant clusters. Flexible data aggregation ensures that the right granularity is available at any time. Data can then be replayed and aggregated in different ways for detailed analysis of test events. This approach minimizes IT operational costs and the storage infrastructure within the test lab.
Electric vehicle powertrain testing is a typical use case where a scalable data back end offers significant advantages. A huge quantity of data is generated, especially during real-time power and electric motor performance evaluation. Data rates can vary from 10 samples/sec up to 4,000,000 samples/sec. The challenge is storing all this data, while keeping it available on a 24/7 basis for rapid analysis of continuous and triggered data streams.
To capture, analyze and store data, and ensure its availability for applications, Gantner selected Apache Kafka, a data streaming platform, to manage cold data; and the distributed database, CrateDB, to handle hot data. Working with this scalable data back end concept demonstrates the power of combining edge computing, big data handling, and machine learning.
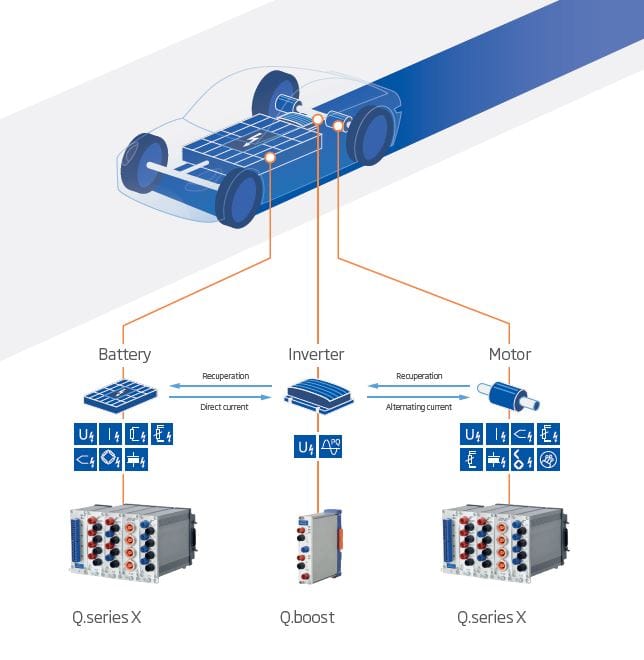
Test labs use specialized control, monitoring and data acquisition systems, but often lack the necessary integration between these systems, which can lead to late fault detections in systems under test. Gantner’s philosophy is to provide customers with open interfaces to store data and send it wherever they need – enabling seamless integration with any monitoring, analysis and reporting tool.
For test labs outfitted with automated test systems, the company’s Application Programming Interface (API) provides a simple way of integrating the solution into their existing environments. Analysis and fault detection methods differ by application, so standardized interfaces for integrating with existing architectures, visualization methods and report routines are essential; for example, to accurately calculate power factor, apparent power, and reactive power from raw measurement data.
With an adaptive and scalable data back end solution, Gantner Instruments provides test labs with the platform needed to grasp, monitor, analyze and react to any physical data in real time, regardless of the data volume – transforming data directly into insights.
Experience the new platform for modern and robust measurement setups
The GI.bench software platform combines faster test setups, project configuration and handling, as well as visualization of data streams in one digital workbench. It enables you to configure, execute and analyze your measurement and test tasks on the fly. Access live and historical measurements data anywhere.

More articles
Trapped in Ice
Arctic ice is disappearing — the question is how fast. Summer sea ice could endure 100 more years, or it could vanish later this decade, with disastrous consequences for the rest of the planet. To nail down the answer, an expedition to the top of the world has to uncover the complex physics of ice.
Read more...Introducing GI.bench – Enhanced DAQ Capabilities for Engineering Excellence
Engineers and technicians often have a lot of problems when they are dealing with complicated data acquisition setups. These setups can include large amounts of data, the use of different devices, and the need for information in real time. Addressing these challenges head-on, Gantner Instruments proudly announces the latest evolution of our industry-leading software, GI.bench.
Read more...Automotive Test Automation
With an increasing pressure to reduce CO2 emissions, E-mobility is a fast-growing market. While keeping this in mind, Gantner Instruments successful Q.series product line offers the best performance with maximum flexibility, to meet the growing demand for E-Mobility Battery Testing and Battery Management Systems.
Read more...The Hydrometer
A novel soft sensor that significantly improves the drinking water treatment process
Read more...