Gantner Instruments is an industrial partner of the Josef Ressel Centre for Intelligent Thermal Energy Systems at the Vorarlberg University of Applied Sciences. Among other research topics, scientists at the Josef Ressel Centre investigate potential control mechanisms suitable to control fleets of heat pumps to utilize the flexibility for Demand Side Management. A Q.station edge device provides the data preprocessing steps in an industrial lab setup. It connects the heat pump system to GI.cloud, the central entity from which the scientists can control the entire fleet.
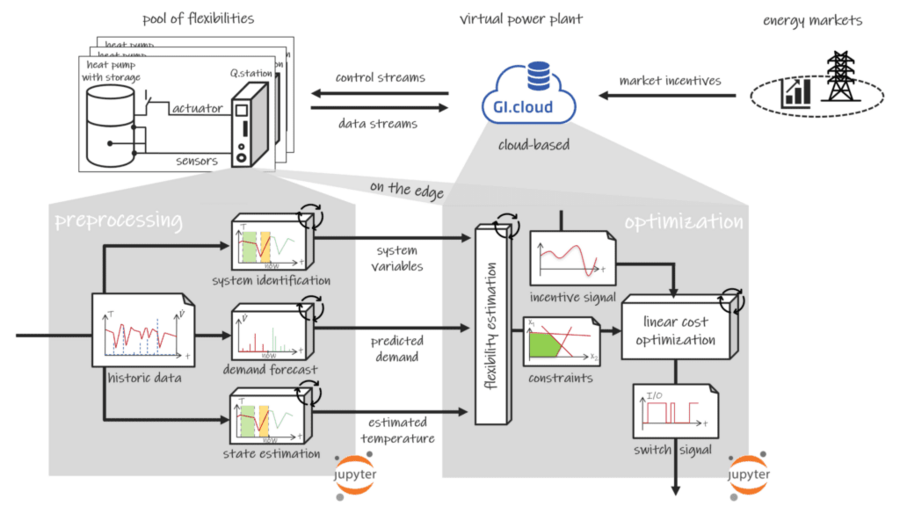
The control approach assumes to react on market incentives, such as a real-time energy market pricing system. The preprocessing of the data acquired at the heat pump system is always executed on the edge (Q.station), covering the autonomous identification of the thermal storage system and state estimation and predicting the user’s hot water demand based on data mining algorithms. These steps provide the data necessary to estimate the system’s flexibility for the near future (the following day) and the optimization problem’s constraints. The optimization routine can be executed autonomously for a single device on either the edge or the cloud comprising a swarm of heat pump systems. The goal of the optimization challenge is to minimize cost implications associated with a certain incentive, while also considering and respecting existing flexibilities. The Q.station processes the resulting switching signals to control the heat pump system.
All software developed for this research project was implemented in Python Jupyter notebooks and can be easily deployed on the Q.station and GI.cloud (as seen above).
Researchers at FH Vorarlberg are currently running multiple scenarios with the lab’s heat pump system. They mimic hot water user schedules and use Gantner’s infrastructure to optimize the schedules on GI.cloud, incorporating day-ahead pricing schemes currently available on the Austrian Energy Exchange markets.
This work is part of our research project Intelligent Thermal Energy Systems; for more exciting details, see the project page.
Authors:
Peter Kepplinger, Christian Baumann (both FHV) and Jürgen Sutterlüti
More articles
Korea Aerospace Industries selects Gantner Instruments for Structural Testing
Korea Aerospace Industries (KAI) has selected the Q.raxx slimline DAQ system from Gantner Instruments for static strength and fatigue evaluation testing of the LCH/LAH helicopter airframe, main landing gear, and engine mount structure.
Read more...Gantner Instruments appoints Bienfait as new Business Partner in the Netherlands
Gantner Instruments is pleased to announce that is has appointed Bienfait B.V. as business partner in the Netherlands. Bienfait will support Gantner Instruments’ entire portfolio of test and measurement solutions. The appointment provides stronger local support for the country’s rapid growth in key sectors like high-tech systems, energy, water and advanced composite materials.
Read more...E-TECH EUROPE 2024
Gantner Instruments is participating in E-TECH EUROPE 2024, the international trade show for advanced batteries and innovative technologies essential for automotive and electric vehicle production.
Read more...The Aerospace Test and Development Show 2023
Join us from 19-20 September 2023 in Toulouse at The Aerospace Test and Development Show 2023 at booth 332. Register here for Your free exhibition pass.
Read more...