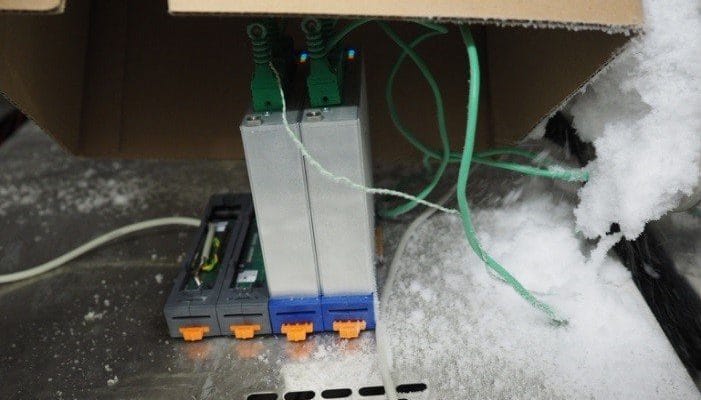
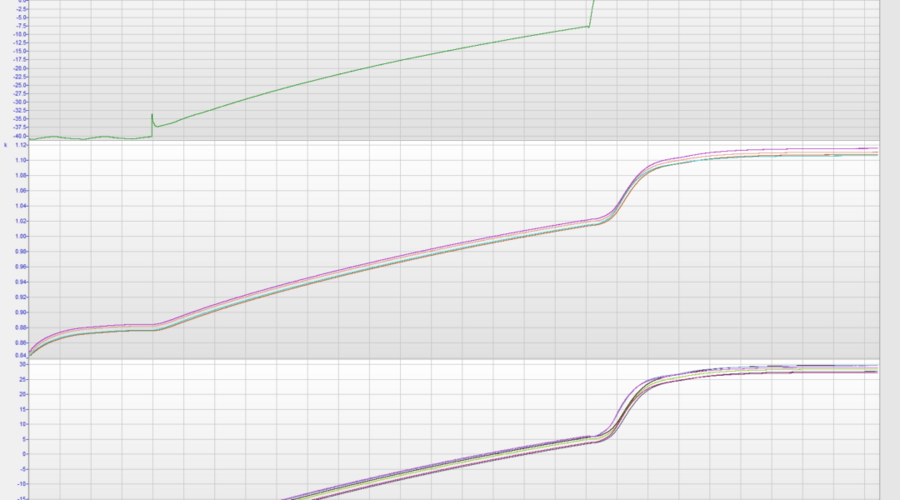
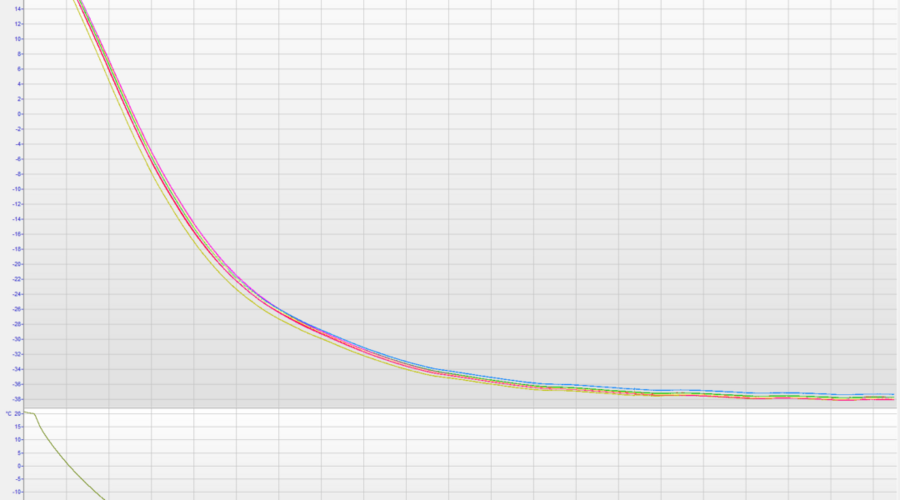
The Q.bloxx XL A104 TCK provides 8 channels for thermocouples (here as Type K, NiCr/Ni) with standard miniature front sockets.
During a day in the climate chamber at -40°C it was completely frozen. After connecting with power supply to the I/O module it was delivering stable and precise measurement values. When temperature was increasing it passed dew point. We observed no impact on the measurement quality or from condensation during this phase. Our I/O module passed this test successfully – even when the datasheet recommends only -20°C operating conditions.
More articles
EIS-Testing Webinar
Gantner Instruments, in collaboration with FLW, is excited to invite you to a free webinar on Tuesday, September 24th, at 11:00 AM EST: "Unlocking the Full Potential of Batteries, Fuel Cells, and Electrolyzers with EIS Testing."
Read more...EtherCAT performance combined with industry leading DAQ: 5 benefits you’re missing out on
We have compiled a list of the 5 most significant benefits of using an EtherCAT-based data acquisition system. If you’re not already familiar with EtherCAT, prepare to be enlightened. If you’re among the many engineers that use EtherCAT in your testing lab then you can consider this a confirmation of why you do what you do – and an excellent place to direct those who still think Industrial Ethernet is not suitable for high-performance testing applications.
Read more...Staying Ahead of the Curve: Meeting the Challenges of EV Powertrain Testing
In this blog post we show in advance the technical challenges of testing electric vehicles and measuring power quality and how the innovative solutions from Gantner Instruments can help to overcome these challenges.
Read more...The Independent Graphical Developer Conference
11th - 13th September | Stuttgart, Germany Catch us at GDevCon, the premier independent conference dedicated to graphical developers! Taking place from September 11th to 13th, GDevCon 2024 is an unparalleled event designed to bring together the brightest minds in graphical programming.
Read more...
